Planting a hedge
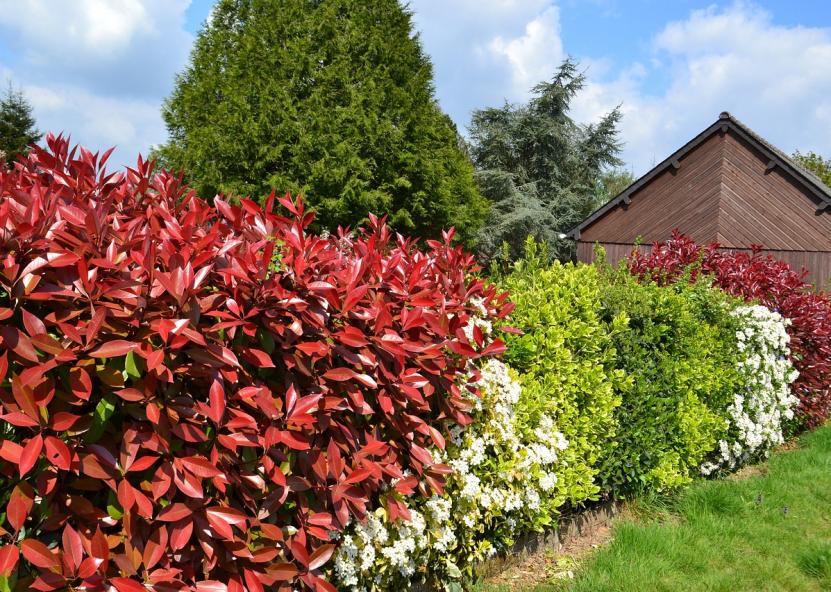
High hedges can be used to divide the property into separate functional areas and camouflage outbuildings. How do I plant a hedge correctly so that it grows healthy and fast enough? It is better to plant hedge plants in a trench rather than in individual holes, as the hedge needs to grow as a solid green mass.
Schemes for planting a hedge
Traditionally, the following hedge planting schemes are used: single, double or triple. The choice of scheme depends on the size of the plot and the type of plant - coniferous or deciduous.
A single-row hedge is suitable for a small plot, a double-row hedge for a medium-sized plot. For green fences, single-row planting is the most common for conifers and shrubs, and 2-3 rows for deciduous shrubs.
Trenches for planting hedge seedlings are dug 30-60 cm deep, depending on the size of the plants (60 cm for tall hedges – 60 cm for medium hedges – 40-45 cm for medium-sized hedges – 30-35 cm for short hedges – 30-35 cm for short hedges).
The width of the sward should be 45-50 cm for a single tree hedge, 30-40 cm for tall shrubs and 20-30 cm for small shrubs.
For a 2-3 row hedge planting scheme, the trench width should be twice as wide (70-100 cm). In the case of a trellis hedge, the seedlings are arranged in chess order.
The depth of the hedge trench shall be 50-60 cm.
Preparing the soil mix for planting the hedge
The top layer of fertile turf removed from the trench at the time of excavation is mixed with peat, humus or compost. Mineral fertiliser may be added. Heavy clay soils and loams are supplemented with sand, sandy loam & loam. Add lime to acid soils and peat to alkaline soils.
The resulting soil mixture is poured into the trench. The height of the mix layer should be 10-15 cm above the soil surface, taking into account the further subsidence of the substrate over the next 2-3 weeks.
Preparation of planting holes
The stakes for the seedlings shall be staked in the soil mixture. For a single hedge, they should be placed in a line in the centre of the mix, and for a double hedge, at a distance equal to the width of the row spacing. A string is stretched between the stakes to make the holes for the hedge plants.
If the planting is to be done in 3 rows, the holes shall be made in chess order. The stakes are then pulled out and the hedge plants are planted one after the other. It is very important to keep the spacing of the seedlings in the row the same.
Setting up the hedge
After planting, the damaged roots of the seedlings are removed and the healthy roots are trimmed by 1-2 cm to encourage root formation.
The root collar (the part where the stem or trunk passes into the root) of each planted seedling must be at the surface of the ground. Compact the soil around the roots.
In a single row hedge, 3-5 plants per metre are usually planted. Denser planting is used for shaped hedges.
In hedges of mature shrubs and trees, the planting is looser, taking into account the future diameter of the crown of the shrub or tree as it grows.
When planting different plants in a hedge, it is important to take into account the shape of the crown, the rate of growth, the plant's response to light, the moisture content, and the composition of the soil.
At the end of planting, all plants in the hedge shall be watered generously. It is useful to add a root-forming stimulant to the water. The soil around the seedlings is mulched with peat, pine bark, wood chips, wood shavings to reduce evaporation of moisture and to inhibit the growth of weeds.
Growing and hedging of shrubs and trees will be possible a year or two after planting, when the plants have finally taken root with confidence and have produced side shoots.
Coniferous shrubs and trees are pruned once a year in spring, deciduous shrubs and trees twice a year (spring and autumn).
Types of hedges and their purpose
If you don't want to burden yourself with constant pruning, choose a free-growing hedge made up of plants that don't need mandatory shaping. These can include all kinds of rose hips, Chinese roses, hawthorn, honeysuckle, orange trees, lilacs, hydrangeas (large-flowered, etc.).
If you want your hedge to grow as quickly as possible after planting, the easiest way is to plant climbing annuals along a chain-link fence or on a pergola. For example, nasturtium, sweet peas. Fast-growing perennial hedges include Chinese roses, rose hips, willows, hops, sedum, Chinese lemongrass, clematis, clematis.
To keep your hedge green all year round, choose evergreen coniferous shrubs and trees. Candidates include tuya, boxwood, cypress, ornamental needles and pines, junipers.Buxwood, yew, dwarf rose varieties and golden currants are suitable for low hedges. They can easily form a low hedge up to 1 m high.
And if you want to achieve maximum privacy on your plot, but the idea of a 3 metre fence doesn't appeal to you, plant a hedge of tall shrubs such as hornbeams, thuja around the perimeter. Such a hedge can grow up to 3-4 m high.