Sowing beetroot in August
Beetroot seeds can be sown in late August in open ground. Young plants form 3-5 leaves before frost and overwinter in this state. The leaves should be cut off for the winter and the crop should be well covered with straw or mulch. In early spring, the layer of straw or mulch is removed and the overwintered beetroot quickly produces new leaves.
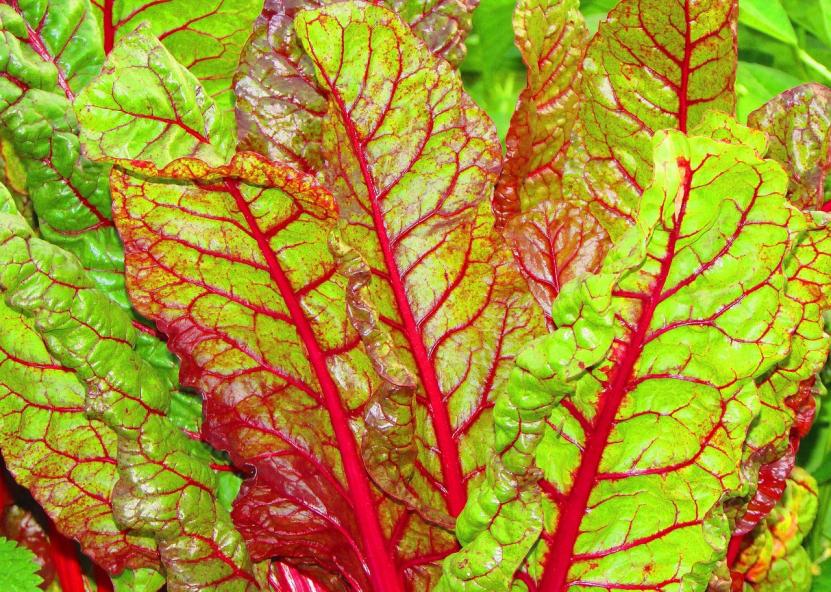
Leaf beetroot has another name – chard. They come from warm countries – Sicily, Cyprus, Crete. Leaf beetroots also form roots, but are not eaten because of their coarseness, small size and branching. Only the leaves and petioles of chard are edible.
Leaf beetroot planting site
Leaf beetroot is a very light-loving plant and should be given a sunny position in the garden. It is important to pull weeds in good time while the seedlings are small, otherwise the weeds will interfere with them.
Leaf beetroot likes fertile soils, nitrogen is particularly important for leaf growth, so it is useful to add humus, rotting soil or compost to the beds before sowing – half a bucket per 1 square metre.
It is intolerant of acidic soils and if this is a problem then the acidity should be reduced before sowing the seeds.
Make sure that the starter seed is free from spinach and all beetroot varieties. The plant must not be sown in the same place where it grew the previous year. Due to its short growing season, it can be sown after peas, radishes, early cabbage and cauliflower.
How to sow leaf beetroot
Because they are cold-hardy, seeds can be sown in August and before winter, from 1 to 20 November, but in this case the crop must be mulched with humus or peat. Sowing can be done in early spring, in late April or early May (depending on weather conditions and region). Before sowing in spring, it is recommended to soak the seeds in water at room temperature for 2–3 days to swell them.
Seeds are sown in furrows 3 cm deep.
The sowing scheme for leaf beetroot depends on the variety. Those varieties whose petioles are used for food are sown with a sowing pattern of 25-35 cm between seeds in a row, with a spacing of 45-60 cm between rows. Varieties grown for their leaves are sown at 20 cm spacing in the seed row and 30 cm between rows.
Mangold seeds can also be sown at a shorter spacing (5 cm) to avoid the risk of not all seeds germinating. But if all germinate, the seedlings will need to be thinned. The first thinning should be carried out at the 4-5 leaf stage, leaving a spacing of 7-8 cm between plants in the row. The second time, after 15 to 20 days, to the required spacing (approx. 20 to 35 cm).
No more than 10 days should elapse between sowing and the appearance of the first sprouts. Seeds germinate at +5-7° C and are not afraid of temperature drops down to –1-2° C.
Care of leaf beetroot
Maintenance of chard includes watering, weeding and row loosening, fertilization and treatment against diseases and pests.
Due to the short growing season, the use of herbicides instead of weeding is prohibited. Weed growth can be stopped by mulching.
The plant needs irrigation until seedlings emerge, but cannot tolerate stagnant water and waterlogged soil. On the other hand, beetroot can tolerate a little drought, but only yields well with sufficient irrigation. The plants should be watered at least once a week. And in hot weather and drought – at least 2 times a week. Otherwise, in hot weather and drought, the succulent leaves may start to die back.
The chard will need to be fertilised 2–3 times during the season.
• 2 weeks after germination – with a solution of cow dung (1:6) or chicken dung (1:10). Mineral fertilisers: ammonium nitrate - 3 tablespoons per 10 litres of water, potassium salt - 2 tablespoons per 10 litres of water, consumption rate: 10 litres per 1 square metre
• 2-3 weeks after the first fertilisation, apply the same fertiliser at the same rate;• If beetroot growth is weak in August – fertilise with cow dung solution (1:6) or chicken dung solution (1:10). The rate is 10 litres of solution/1 square metre.
The clover is harvested when the plant has grown 8 leaves. For early varieties this takes about one month.
Leaf beetroot is susceptible to leaf spot and powdery mildew. Biofungicides are used to protect against fungal diseases.
The plant can be attacked by mites, caterpillars, slugs and black aphids. To combat them, mangolds are treated with insecticides or folk remedies (tree ash, tobacco dust, soap solution).