How to protect trees on a plot during construction
Suppose you are planning to build a house or other new structure in a wooded area amongst the trees of your garden. How can you avoid damaging the roots and trunks of existing trees or accidentally destroying them during construction? What if transplanting large trees is not possible, but you want to preserve them?
Probably the most challenging areas to hand over for construction are woodlands. A forest, a grove or even a garden is a complex organism where soil, groundwater, trees and their roots interact. The main task here is to minimise the damage caused by interference with nature.
Tree root protection
Digging operations must be carried out with certain measures, the main task of which is to create a favourable zone for the subsequent recovery of the root system. The roots of a tree can only live in moist soil and die within a few hours after reaching the surface. Given this characteristic, it is important to dig the soil layers correctly in a woodland site.
A critical boundary is the one that passes through the point where the trunk starts to branch out into roots (this is called the root collar). For the tree to survive, the soil must not cover it too much. So if the builders have covered the tree with 1.5 m of soil when levelling the ground, rest assured that the tree will die.
In order not to damage the roots of trees, solutions called dry wells have been developed to protect the roots of trees. The walls of dry wells are concrete. One side of the wall holds the soil in place from the outside and reinforces the slope, while the inside of the wall protects the tree roots. The space between the tree trunk and the well wall can be covered from above with a metal grill. The diameter of the opening for the trunk in the grille must be equal to 2 trunk diameters.The root growth zone shall be equal to the area determined by the radius of the projection of the tree crown onto the root system, increased by 1 metre. Excavation work in this area shall be carried out with great care and without the use of heavy construction equipment. The excavation exclusion limit shall be at a distance from the trunk axis equal to twice the circumference of the trunk, measured at a height of 1,3 m from the ground.
When it is necessary to cut tree rootsWhen excavating around a tree, the roots shall be cut at the level of the excavation wall, using pruning shears or a hand saw, and treated with a wound protectant, without under any circumstances covering the cut wounds with paint. The excavation wall at the level of the cut roots shall be lined with moist peat, covered with jute, straw mats and periodically watered with water to keep the materials slightly moist.
When excavation work around a tree is expected to take a long time, the above protection is not sufficient – reinforced protection is necessary. A special screen made of planks must be made 5 cm from the excavation and the space between it and the formwork must be filled with fertile soil. This must be followed by a generous watering of the soil.How to protect tree trunks on construction sites
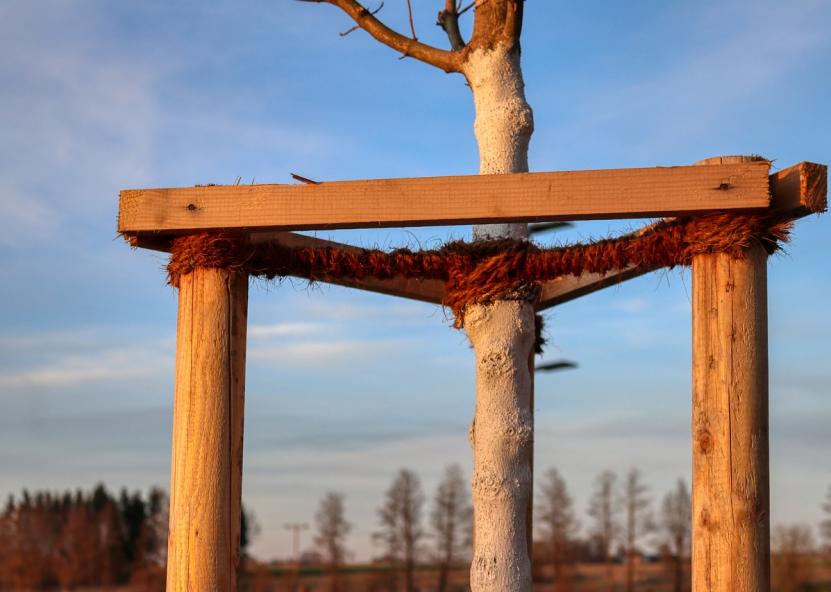
Protecting tree trunks from damage during construction work is an obvious topic. Strapping trunks with a protective layer of boards or wooden panels between 1.7 m and 3 m high will be optimal, but you need to be sure that the "shield" itself will not cause damage to the bark and branches of the trees.
When completing this task, builders need to make sure that they understand what they are doing and why. To increase the effectiveness of the trunk protection layer, a shock-absorbing straw mat can be placed underneath to absorb any impact.How to protect the crown
During plastering or other wall finishes and repairs, the crowns, branches and crowns of trees and shrubs growing in the immediate vicinity of the building can be damaged. To avoid this, it is a good idea to cover the plants with screens made of boards or very thick reinforced plastic before starting work. The screens should be attached to wooden frames.
How to prevent soil compaction
If heavy construction machinery is unavoidably going to be working near the tree, or if there is a chance that this machinery will frequently pass near the tree, care should be taken to ensure that the soil is not excessively compacted and that the root system is not damaged by subsidence and compaction. This can be avoided by temporarily laying reinforced concrete road slabs or a crushed stone cushion (25-30 cm thick) around the trunk according to the diameter of the crown.