Copa-Cogeca publishes manifesto on organic farming
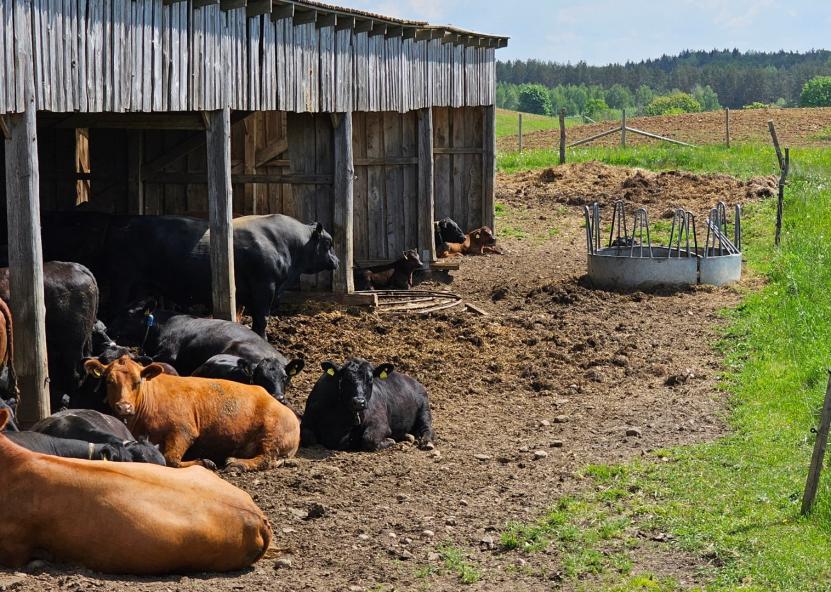
Organic farming is a production method that focuses on protecting soil, water, biodiversity and animal welfare. In order to protect existing agricultural investments and improve the economic viability of farmers, a balance between supply and demand must be maintained. Further growth in organic production will require much higher consumer demand. To encourage organic consumption, it is important to publicise the benefits and credibility of organic farming and to educate consumers.
Copa – Cogeca's Organic Farming Working Group has produced a farmers' manifesto setting out the key arguments, challenges and actions that need to be implemented to promote organic farming and to achieve the target of 25% of agricultural land in the EU being farmed organically by 2030.
Main arguments:
Organic farming is an integral part of many of the EU's Green Deal objectives. Increasing organic farming can reduce the use of chemicals in agriculture, increase biodiversity on farmland and improve animal welfare.
Environmental benefits: Organic farming has several environmental benefits, including reduced use of pesticides, better soil health and increased biodiversity.
Animal welfare: Organic requirements ensure better conditions for animal welfare, in particular by increasing the area where livestock are kept and by ensuring access to pastures and outdoor areas that allow animals to move freely.
Economic impact: Positive contribution to rural development and job creation in the agricultural sector. By promoting sustainable practices, organic farming can help to create a more resilient local economy. It supports small and medium-sized farms, which are vital to sustain rural communities. In addition, organic farming can open up new markets and opportunities for farmers, including higher prices for organic products, which can help improve the economic viability of farms.
The main challenges for farmers in the sector
Regulatory burden: The revision of Regulation (EU) No 848/2018 has introduced stricter requirements, making it more difficult for farmers to implement them.
Market access and fair remuneration: The EU is well behind the Organic Action Plan's target of 25% of agricultural land being farmed organically by 2030, with a 2022 result of only 10.5%. Growing food organically involves much higher production costs, which unfortunately are not always reflected in the prices farmers receive for their products. Therefore, it is important to ensure the implementation of long-term contracts in order to achieve higher income levels.
Consumer confidence and demand: Stimulating consumer demand is also vital for the growth of the sector. In order to promote the development of organic farms, it is important to build and strengthen consumer confidence and to focus on education and information on the benefits of organic products.
Key actions
Address the technical issues of the EU Organic Regulation (EU) No 848/2018 where the burden on organic farmers could be eased. Specific farm-level concerns, drawn from across Europe, should be taken into account to make the Regulation more farmer-friendly and to address specific challenges that negatively affect farmers' day-to-day work and their income. This will help to maintain and increase the attractiveness of the sector for organic farm owners and future generations.
Promote organic products: Ensure better use of the EU budget to promote organic production and inform the consumer generation through targeted campaigns and education programmes. Indeed, 28% of the budget is allocated to the organic sector under the promotion policy, but most of these resources are not being used in a targeted way.
Invest in research and innovation: Increase investment in research and innovation in the organic sector to develop professional and specific knowledge, improve farming practices and address technical challenges. The organic sector should be allocated funds for research and innovation to support climate initiatives, the sustainable supply of organic nutrients and proteins, and targeted breeding and management for animal health and welfare.
By addressing these key areas, we can support the sustainable growth of the organic farming sector, ensuring that it remains a viable and attractive option for farmers and consumers for a more sustainable future.